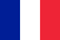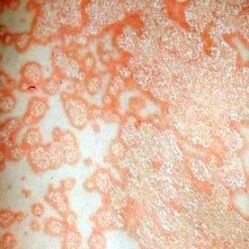
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious skin disease. This disease often recurs. Very rarely, psoriasis can affect joints, nails and mucous membranes. People of all ages are susceptible to psoriasis. According to statistics, there has been a tendency to the development of the disease during childhood.
Psoriasis is not a chronic infectious disease. Most dermatologists tend to believe psoriasis is a systemic disease. In their opinion, the disease not only affects a specific area of skin, but also entails the pathological process of almost all body systems (endocrine, immune, nervous).
From the outside, it seems that psoriasis is a mild illness. But in reality, this is far from the case. Serious disease. Deaths are known in the field of dermatology. In the case of improper or timely treatment, the psoriasis affects the entire body, easily leading to serious complications. For example:
- Psoriatic arthritis
- swollen lymph nodes
- conjunctivitis
- mucosal damage
- flatten and damage the foundation panels
- spontaneous pain
- amyotrophy
- Rarely - damage to the heart
As a rule, psoriasis does not interrupt a person's normal life rhythm. The only inconvenience is flaky and inflamed skin. Unfortunately, it is not possible to recover from the disease, but it is possible to completely suspend its development or prevent the occurrence of relapses. To do this, it is enough to satisfy all doctor's prescriptions and undergo systemic treatment in the hospital.
Causes of psoriasis
There is no specific cause of the onset of the disease. There are many factors that can lead to the development of psoriasis. There is no clear opinion about this reason or another in dermatology. There are many versions. Most dermatologists assume that the disease has a genetic factor. It is not possible to confirm or conclusively deny that genetics is the main cause. There are cases where the whole family suffers from psoriasis.
In other words, we could say this: if a mother suffers from psoriasis, then it is not necessary that her children will definitely show signs of the disease. But it is also not possible to rule out genetic factors. For example, if a grandmother has this disorder, it is possible that grandchildren will never be diagnosed with psoriasis. The question of the cause of the disease development at the genetic level remains open to this day.
The next factor, according to many dermatologists, can provoke the appearance of psoriasis, which is a disease of the endocrine system. Examples include adrenal gland dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, pituitary dysfunction. The rate of signs of psoriasis in people with diseases of the endocrine system is quite high. Therefore, associations between diseases exist and are proven by many examples.
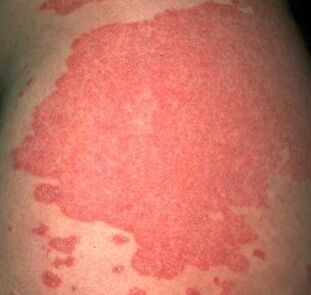
In addition to the above reasons, there are many endogenous factors. For example:
- Diseases of a deferred infectious nature, for example, tonsillitis. According to statistics, 17% of patients surveyed believe that psoriasis is the result of complications of angina.
- Chronic infectious pathological processes, such as laryngitis or tonsillitis, can also cause psoriasis.
- Long-term use of certain drugs: interferon, NSAID, beta blocker and others.
- It sounds weird, but getting pregnant can also lead to the development of psoriasis. In a woman's body, significant hormonal changes occur, which usually triggers an underlying pathological process in the body.
- Negative effects on the human body of consuming too much UV radiation cannot be ruled out, that is, long-term exposure to scorching sun or frequent visits to the solarium.
Of course, in addition to endogenous factors, there are also some exogenous causes. For example, skin diseases (dermatitis, fungal dermatitis, pyodermatitis), mechanical damage to skin integrity, atopic dermatitis.
Interesting fact. Psoriasis is significantly more common in HIV-infected people than in healthy people. It is important to note that women are more susceptible to psoriasis than men. Dry, thin and sensitive skin is a common factor.
You should know that if a person has an immune system disorder, then this pathology often causes psoriasis. Immune disorders and psoriasis are closely related.
There are many reasons that lead to psoriasis, but no one completely leads to the development of the disease.
Forms and forms of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a multifaceted disease. According to statistics, people usually have only one form of psoriasis at a time. But there are instances when a person develops multiple forms of psoriasis at the same time. Quite often in dermatological practice, and so is when one form of psoriasis changes easily. As a "regeneration", as a rule, leads to a sudden cessation of prescribed treatment.
In dermatology, there are two main groups of psoriasis that are non-purulent and purulent.
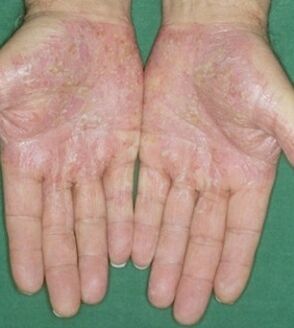
Pustular formBarbera psoriasis, soles and palms psoriasis (see photo), Tsumbusha psoriasis, annular pustules. This form of psoriasis is generalized and localized. Pustular psoriasis can eventually occur on any area of the skin. There are cases of pustular pustules forming in vulgaris psoriasis.
As an example of an independent disease, you might consider dermatitis caused by Allopo. As a rule, the disease is characterized by pustular lesions and a scaly layer on the distal knuckles of the fingers and toes. Another example of an independent disease of a localized form of psoriasis is pustular psoriasis of the soles of the feet and palms. It is important to note that some dermatologists tend to believe that the disease is a form of pustular bacteria.
General pustular psoriasis includes:
- herpetiform impetigo,
- Tsumbusha psoriasis,
- General exanthemic psoriasis.
As a rule, men from 15 to 35 years old with Tsumbush psoriasis. This disease is less common in women.
Exanthemic pustular psoriasis occurs suddenly (suddenly) and acute. In most cases, there is a close relationship with other infectious diseases, such as tonsillitis. The rash is localized mainly on the trunk. Usually children, adolescents are more susceptible to disease than adults.
Herpetiform impetigo is a serious illness that can lead to death. As a rule, this disease is characteristic of pregnant women, more often in the second trimester. But in dermatological practice, there are still extremely rare cases of the disease in men, non-pregnant women and children.
Non-purulent psoriasis. . . In other words, we can say simple psoriasis. This form of the disease differs from other forms of the disease in a steady process. In the non-purulent form of psoriasis, almost the entire surface of the body is affected. This includes:
- erythrocyte psoriasis
- vulgaris psoriasis, or normal, or plaque.
Psoriasis is a common occurrence, with up to 90% of patients with psoriasis being in a vulgar state of the disease.
Red cell psoriasis is a dangerous disease that often leads to a fatal outcome - the death of the patient. With this disease, there is a violation of the function of thermoregulation, as well as a decrease in the barrier function of the skin. These conditions lead to purulent dermatitis or sepsis.
Classification and symptoms of psoriasis
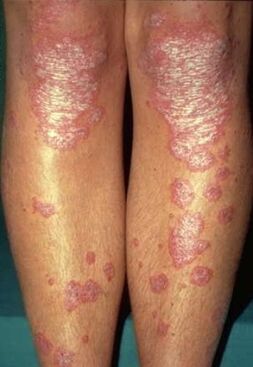
There is no single class of psoriasis that is generally accepted by dermatologists. There is still debate about the classification of this skin disease. Some sources have a list of their own types of psoriasis. The most common classification of the disease:
- Intestinal psoriasis
- Purulent psoriasis
- Psoriasis mental illness
- Psoriasis of the mucous membranes
- Psoriasis secretion
- Psoriasis soles of the feet and palms
- Psoriasis of the joints
- Psoriasis between episodes
- Psoriatic erythema
- Seborrheic psoriasis
- Psoriasis
- Pustular bacteria
- Tsumbusha psoriasis
Psoriasis of the jointsThere are almost no symptoms at first. The patient sometimes noted only mild pain in the joints. Over time, the pain gets more intense, becoming sharp and acute. The affected joints become swollen. If the disease is not treated, the joints will be deformed, limiting mobility. As a rule, psoriasis of the joints is often accompanied by rheumatic type pain. In winter, there is an exacerbation of the disease, that is, seasonal characteristics are characteristic of such psoriasis.
Purulent psoriasis. . . It is uncommon, only 1% of all patients with psoriasis belong to this type of disease. In most cases, the rash is symmetrical and localized on the soles of the feet and palms. Purulent psoriasis is general and local in nature. The latter is more common than the previous one. Systemic purulent psoriasis is difficult to treat. In the dermatologist, there are frequent deaths from sepsis and severe body intoxication.
Psoriatic erythema. . . Severe psoriasis caused by an exacerbation of psoriasis already exists. The illness can be both a result of an exacerbation of the underlying disease, and the first time it has arisen. Secondary erythrocyte psoriasis develops, as a rule, in 2% of people with this disease.
This disease usually occurs spontaneously, but does not exclude psoriasis caused by improper dermatological treatment, which is bothersome during the acute course of the disease. The patient noted an increase in pathological desquamation foci, an increase in temperature and dehydration were detected. In dermatological practice, there have been deaths in erythrocyte psoriasis.
Intestinal psoriasisThe second most common disease among all forms of psoriasis, suffers more often in children and teenagers. It is characterized by the appearance on the skin of a large number of dry, purple and small elements that protrude on the unaffected skin surface. The rash comes in the form of drops, circles, or drops of water. As a rule, the elements cover the entire human body, but most of the "density" resides on the thighs. In most cases, the appearance of teardrop-shaped psoriasis is caused by a streptococcal infection. Examples include strep throat, strep throat.
Psoriasis mental illness. . . The disease is characterized by various changes in the appearance of the nail plaque, both on the hands and feet. First of all, the color of the nail changes, sometimes the whole nail bed together. The nail turns gray, yellow, or white. Tiny spots or spots appear on the nail, and sometimes even under the fingernail. The nail plates thicken, appear stripe, and brittle. Another clinical manifestation of the disease is thickening of the skin around the nail. The difficult result of psoriasis on the skin is spontaneous nail loss.
Psoriasis of the mucous membranesPurulent psoriasis, also known as vulgaris psoriasis. Most often, the mucous membranes of the cheeks, tongue and lips are affected, less often than the mucous membranes of the genitals and eyes. With the pustular psoriatic form, the erythema is more widespread, a wide area of the mucous membrane is affected, and geographical glossitis is noted. In common psoriasis, well-defined, well-demarcated flat-white papules appear on the mucous membrane, towering above the unaffected surface.
Psoriasis soles of the feet and palms. . . The disease is a localized form of pustular psoriasis. As a rule, this form is chronic and recurrent. In dermatology, there are cases of Barbera's psoriasis progressing with plaque psoriasis at the same time. Pustules appear on the inner surface of the hands and / or feet. Over time and under the action of medical treatment, the blisters-pustules dry up. Then, such dry particles form a dense brown crust.
Intertrigue psoriasis. . . The disease is characterized by the appearance of erythema mainly in large folds of the skin. Examples are the folds between the fingers, the groin folds, the armpits and the lower mammary glands. Intertrigue psoriasis is more common in patients with diabetes, VSD (vascular dystonia), obesity, who do not adhere to simple rules of hygiene.
Pale-scaly, erosive, crusting nocturnal edema, forming in the folds. An important feature of factors of this disease is the sloughing of the horny layer detected along the periphery. Intertrigue psoriasis is very similar to an epidermal infection, a Candida infection or rubromycosis. It is important to note that the clinical picture of candidiasis or dermatosis is much brighter and sharper than psoriasis.
Seborrheic psoriasis. . . In terms of its symptoms, seborrheic psoriasis is very similar to seborrheic eczema. As a rule, psoriatic rashes have the same localization as factors of seborrheic eczema. It can:
- nose folds
- head skin
- auricles
- chest area
- interstitial area
With seborrheic psoriasis, areas on the head appear, on which the skin is severely flaky. An important feature of this disease is the formation of a psoriasis. Skin damage occurs from the forehead and spreads to the scalp, in such a simple way that the outer contours of the crown appear. It should be noted that dandruff is a "telling" alarm signal for the development of seborrheic psoriasis.
As a rule, behind the eczema, a red eczema is formed, and pus-filled crusts are often arranged in layers. For a rash with localization on the chest and face, gray-yellow scales are characteristic. A psoriatic rash always causes intense itching. It is important to note that seborrheic psoriasis is difficult to diagnose, as it is often mistaken for seborrhea.
Psoriasis secretion. . . This type of psoriasis is more common in children and the elderly. The risk of this disease is quite high in patients with endocrine and immune system disorders. Psoriasis secretion often affects the healthy skin of people who are overweight or have diabetes.
The disease is characterized by excessive accumulation of secretions in papillae, which gradually rise to the surface, forming yellow scaly layers. If the crust is removed, a crying and bleeding surface will be revealed. The scales dry out over time and overlap, thus forming a rather dense and large mass.
The main feature of exudative psoriasis is the clear localization of pathological foci. As a rule, the lower extremities and large folds are most affected. The rash gives the patient the strongest itching and burning sensation. The clinical picture of this disease is sharp and acute.
Psoriasis. . . It has different names in different sources. For example, plaque, normal, simple. This type of psoriasis ranks first in popularity - in almost 90% of patients with psoriasis, this type is observed. The disease usually begins acute. The first symptoms appeared almost immediately.
Oily psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of typical elements that protrude slightly on unaffected areas of the skin. The rash is inflamed, red, and hot to the touch. These particles are thickened, covered with a silvery-white, scaly and dry film (skin) that flakes off easily.
Be aware that the gray crust is easily peeled off, leading to damage to the lower layer of the papillae, where there are many small vessels. This usually results in a small cut. The affected lesions in the dermatology are called psoriatic plaques.
Such arrays tend to link together, increasing their size. Over time, plaques are formed, which has a special name - "paraffin lake". Psoriasis flare-ups with psoriasis are usually very flaky. Long-term treatment, requiring inpatient treatment.
Pustular bacteria. . . According to statistics, this disease occurs mainly in young adults (from 20 years old) and middle aged (to 50 years). The exact cause of the pustular bacteria has not been determined. It is hypothesized that the disease develops against the background of a strong and persistent allergic disease associated with foci of infection. Examples are crooked teeth, tonsillitis or tonsillitis.
Psoriatic eruptions affect the skin of the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Pustular bacteria are chronic, recurring. The first loaf appears, if on the palm, then in the middle, if on the sole, then on the arch. The main psoriatic elements are small in size, not exceeding the size of the pin tip. Over time, the pustule dries and forms a thin, scaly layer. The patient feels severe itching and pain in the affected areas.
The exacerbation of the disease is characteristic of pustular bacteria. At the same time, inflammation occurs in all areas affected by psoriasis. Gradually, the psoriatic foci increase, and after several weeks, almost the entire surface of the palms or soles of the feet are swept into the pathological process. As a rule, pustular bacteria persist for many years and are constantly recurring.
Nutrition for psoriasis
Psoriasis patients only need to adhere to a diet and follow the basic principles of proper nutrition. The main job of the diet is to maintain a normal acid-base balance. But it's important to note that the alkaline base of the body should be slightly more dominant than the acidic base.
Naturally, the body's balance depends on the foods that psoriasis patient consumes on a daily basis. It is important to know for every person with this disease that 70% of the daily diet should be composed of alkaline-forming products in the body. As for the acid formed - not more than 30%. To put it more simply, it can be said like this: the alkaline product consumes four times the acidic product.
List of alkaline-forming products in the body:
- Any vegetable except rhubarb, pumpkin and Brussels sprouts. It is important to remember that potatoes, peppers, eggplants and tomatoes are strictly prohibited.
- Fruit should not be excluded. The main thing is to not use prunes, cranberries, gooseberries, and blueberries. It should be noted that bananas, melons and apples should not be eaten at the same time as other foods.
- Make sure to drink fresh vegetable juices from carrots, beets, parsley, celery, and spinach.
- Fruit juices from grapes, pineapples, pears, oranges, papaya and grapefruit, mango, lemon and apricots can be drunk daily. It is important to add lemon juice to your food.
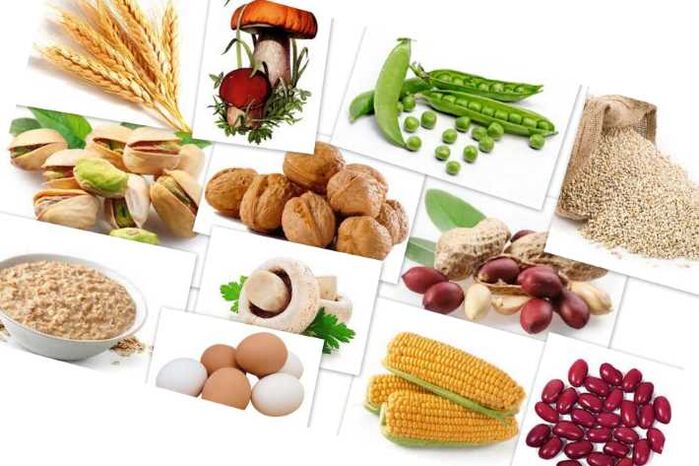

List of foods that psoriasis patients are forbidden to eat (acidic form):
- You should eliminate or minimize the consumption of foods containing starches, fats, sugars and oils. Typically, they include the following foods: potatoes, beans, cream, cheese, cereals, meat, dried peas. An unbalanced daily consumption of these products inevitably leads to the onset of acidic reactions in the blood. As a result, health deteriorates.
- It is important to balance food properly. There are several types of foods that are forbidden to be consumed at the same time. For example, meat products should not be combined with foods high in sugar, sweets, and starches.
- It is important to limit your sugar intake. Various preservatives, vinegar, dyes and food additives should be included in the diet as little as possible.
- The key point is to completely exclude alcohol and alcohol consumption.
Every psoriasis patient should remember that eating properly is an important condition in the treatment of this disease. Must replace fried with stewed or boiled. Eat lightly processed foods.
Treatment of psoriasis
Treatment of psoriasis should take place during an exacerbation in a hospital and on an outpatient basis - during remission. Diet is an important point in treatment. Useful vegetarian day.
In addition to diet and specialized treatments, it is important to carefully monitor skin hygiene. For washing, it is best to use tar soap, you can also use baby soap. You should take frequent baths with the color of cedarwood, purple tricuspid or hops.
If there are no contraindications, you can try psoriasis treatment and folk remedies. Do not test and self-medicate. Only a doctor has the right to advise which folk methods are useful and necessary.
List of safe and effective ointments for psoriasis:

- A packet of butter (but not spread) should be added to the pan with crushed propolis (10 g). Put on heat and cook after boiling for 15 minutes. After - it is necessary to filter the mixture thoroughly and let it cool. Store this medicine only in the refrigerator. Method of application - rub into the affected area several times a day.
- In a clay dish, it is necessary to crush the fresh flowers of St. John. John's wort (20 g), cactus root, propolis, calendula flower (10 g). Vegetable oil is added to the resulting mixture. Store in a cool place, away from direct sunlight. Method of application - thoroughly lubricate the psoriasis 3 times a day.
- In one liter of white wine for half an hour, boil the gallbladder and scales of sea fish, their weight exceeds three kilograms, on a rather small flame. Cool, filter, then add a cup of olive oil. Method of application - thoroughly wash the affected area with egg soap and dry. Then, lubricate the elements with this mixture. The course of treatment until the drug is gone.
- Mix equal parts of the burberry powder and the kerosene (by weight). Method of application - the ointment is applied in a thin layer on the rash and left for up to three days. After that, you need a short break, about 4 days. Treat until the psoriasis completely disappears.
- Add 1 teaspoon of vegetable oil to the melted homemade eggs (2 pieces). The mixture was whipped again, after which acetic acid (40 g) was introduced. Store the ointment in a tightly-closed vial. Method of application - treatment of psoriasis flare-ups once a day, preferably at night.
- An equally effective and popular remedy for psoriasis is a mud cure. The sludge must be warmed to 38 degrees and applied to the affected skin area. This procedure should be performed in the evening, preferably before bed. After 30 minutes, the contaminants are removed with warm water. It is important to remember that after staining, all rashes should be treated with salt water. The body will dry out and excess salt will fall off. If you don't wash or moisturize your skin, you'll need to go to bed. And only in the morning, lubricate the psoriasis elements with cream. The recommended course is 20 procedures (every other day).
Whatever common psoriasis treatment options you choose, you will need to negotiate with your dermatologist.