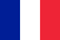
Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious, dermatological disease that primarily affects the skin.Currently, the autoimmune nature of this disease is assumed.Typically, psoriasis manifests itself in the formation of red, excessively dry, raised spots on the surface of the skin - called papules, which fuse together to form plaques.These papules are essentially sites of chronic inflammation and excessive proliferation of dermal lymphocytes, macrophages and keratinocytes, as well as excessive angiogenesis (formation of new small capillaries).
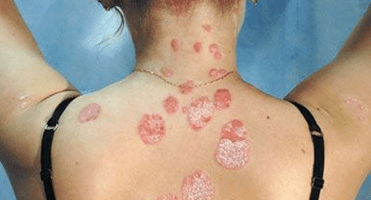
It occurs with equal frequency in men and women and lasts for many years with alternating periods of relapse and remission.This is one of the most common dermatological diseases, difficult to treat and often severe.
What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disease characterized by a monomorphic rash consisting of flat papules that tend to coalesce into large plaques that are quickly covered by loose, silvery-white scales.
Psoriasis is characterized by periods of deterioration (recurrence) and temporary health conditions, when the manifestations of the disease become less severe.This disease is not contagious and the patient does not pose a danger to others.Because the appearance of psoriasis is not related to microorganisms.
The main element of psoriasis is a pink or red papule, covered with a large number of loose silver-white scales.
In principle, psoriasis does not disrupt the patient's normal rhythm of life.The only inconvenience is peeling and inflammatory processes on the skin.Unfortunately, this disease cannot be cured, but it is possible to stop its development or prevent recurrence.To do this, it is enough to follow all the doctor's prescriptions and undergo systematic treatment in the hospital.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is completely not contagious.There have been no recorded cases of person-to-person transmission of the disease.The causative agents of the disease are not infections and bacteria that are potentially dangerous to others, but white blood cells produced by the patient's body.
A healthy person cannot get psoriasis from the patient.Psoriasis is not contagious:
- In case of skin contact, through use of the same household items as the patient (bed sheets, towels, dishes).
- Through saliva and sweat.
- Sexually.
- When taking care of sick people.
- Through blood.
Classify
Experts distinguish two forms:
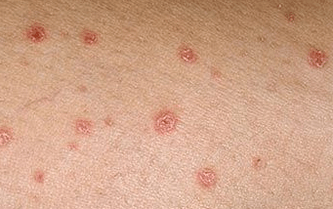
Non-purulent form of psoriasis
What is it?This form of the disease differs from other forms of the disease in its stability.The nonpurulent form of psoriasis is characterized by damage to almost the entire body surface.This category includes:
- erythrodermic psoriasis
- vulgar, ordinary, or tabula.
Psoriasis vulgaris occurs quite frequently;Up to 90% of psoriasis patients suffer from this disease in its vulgar form.
Psoriatic erythrodermatitis is a serious disease that often leads to serious consequences - the death of the patient.With the disease, the thermoregulatory function is violated and the barrier function of the skin is reduced.
pustules
- Zumbusch pustule base or generalized pustule
- palmoplantaris (pustular psoriasis of the extremities, chronic persistent pustular palmoplantaris)
- annular pustules
- palm
- psoriatic impetigo herpetiformis
| Psoriasis stage | Percentage of damage |
| Light | less than 3% of skin is affected |
| medium | 3-10% of the skin is covered by psoriatic plaques |
| Heavy | have joint damage or damage to more than 10% of the skin. |
How does psoriasis start: the first signs
In most cases, identifying psoriasis is quite simple, because the disease is not similar to other skin diseases.Allergic rashes are smaller in incidence than psoriasis spots, and medical history shows that the patient does not actually have skin swelling like allergies.
Early symptoms and signs of psoriasis vary in key features that your doctor will rely on when making a diagnosis:
- the appearance of a limited pink spot of varying intensity;
- itchy skin in the area of psoriasis lesions;
- exfoliates large amounts of epidermis of various sizes;
- characteristic white peeling color;
- the appearance of pale white or gray crusts that do not extend beyond the boundaries of the psoriasis spot;
- dry skin.
Psoriasis is characterized by three distinctive features:
- "Stain effect."When scraping plaque, small and transparent scales easily peel off.
- "End-to-end movie effects".If the scales are removed, the skin in this area will be thin, shiny and red.
- "Bloody mist effect."After shaving, small drops of blood appear on the skin.
reason
Experts cannot identify the exact and single culprit of this disease, but repeated studies show that the disease is autoimmune, that is, it depends on the activity of the immune system.
For some unknown reason, immune cells, designed to protect the body from malignant changes and damage caused by bacteria and viruses, penetrate the upper layers of the dermis and produce substances that trigger the inflammatory process.The result of this activity is proliferation - an increase in the rate of skin cell division.
According to another theory, psoriasis develops due to disruption in the life cycle of keratinocytes.
Possible causes of psoriasis:
- Hereditary.According to the latest data from scientists, psoriasis is classified as a genotypic dermatological disease with a predominant mode of transmission.
- Violation of lipid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.When skin psoriasis is suspected, changes in these blood components often occur, contributing to the development of cardiovascular pathology, endocrine dysfunction and metabolic syndrome.
- The presence of a chronic infection in the body.When examining psoriatic plaques, streptococcal flora is often detected.The appearance of genetic abnormalities can be influenced by viral and bacterial infections, for example, tonsillitis, influenza.
- Climatic conditions - dry and hot weather can affect the progression of psoriasis, intensifying skin manifestations or, conversely, weakening them;
- Anxiety or stress - as mentioned above, excessive stress directly affects the course of psoriasis;
- Skin damage - wounds create conditions for infection and this leads to intoxication of the body due to the inflammatory process, therefore the appearance of psoriasis can cause minor damage, but provided that there are accompanying diseases;
- Infection - flare-ups of psoriasis can be caused by the presence of inflammatory, purulent areas, especially in childhood.
One hypothesis suggests the existence of two variants of the disease:
- Type I psoriasis– genetic with immune factors, more than 60% of patients under 30 years old have this form, good prognosis, lifelong treatment.
- Type II psoriasis– occurs more often at age 45, is not associated with malfunctions of the immune system, most often affects the nail plates and joints.
Symptoms of psoriasis
Skin psoriasis can develop at any age.But the first manifestations usually occur in young people and adults between 18 and 40 years old.There were no differences by gender.Men and women get this disease with equal frequency.
| Signs of psoriasis | |
| form | round |
| edges | clear |
| Color | hot pink or red |
| Color ratio | silver white |
As a rule, the first rashes form at the site of wounds, scratches, frostbite, burns and on areas of the body that are constantly exposed to friction.They may itch, but this is not the main symptom.
Depending on the characteristics of the rash, the following forms of psoriasis are divided:
- Point psoriasis - the size of the particles is smaller than the head of a pin.
- Teardrop shape - papules are teardrop shaped and reach the size of a lentil.
- Coin-shaped - plaque grows up to 3-5 mm and has rounded edges.
Forms of the rash are also distinguished when its elements look like rings, arcs and wreaths, geographical maps with jagged edges.
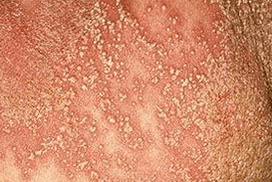
The overall clinical picture and symptoms of psoriasis vary significantly depending on the stage of the disease.Dermatologists distinguish 3 stages of sequential development:
- Progress.New skin lesions constantly appear, in addition there is an active spread of existing plaques with peeling and severe itching.
- Stationery.The growth of papules on the body stops a little, new formations do not occur, but thickened folds appear on the surface of the skin, near the plaques.
- Retreating.The spread of the disease and an increase in peeling were not observed.As the signs of psoriasis subside, areas of significant pigmentation remain on the body.
The alternation of these phases gives rise to the wave-like nature of relapse and remission.A patient may have different stages of the disease in different skin areas.
The early stages of psoriasis are marked by the appearance of papules, which are small scaly spots.They are dark pink, dense to the touch, and slightly raised above the surface of the skin.
The first sign of psoriasis may be the appearance of a rash in areas of the body most susceptible to friction and dry skin in these areas.These are the places:
- palm or elbow;
- below the knee;
- lower leg;
- lateral part of lower back;
- inguinal fold;
- scalp.
The initial stages of psoriasis on the skin are hardly noticeable and do not cause discomfort to the patient.But early treatment will help to avoid severe forms of the disease, in which the nails, feet, mucous surfaces, and then the human joints are affected.
According to statistics, psoriasis plaques are often located in:
- on the outer surface of the joint;
- in the back and abdomen;
- on the front of the thighs and forearms.
This is different from eczema, in which the rash affects the insides of the limbs and the folds between the fingers.